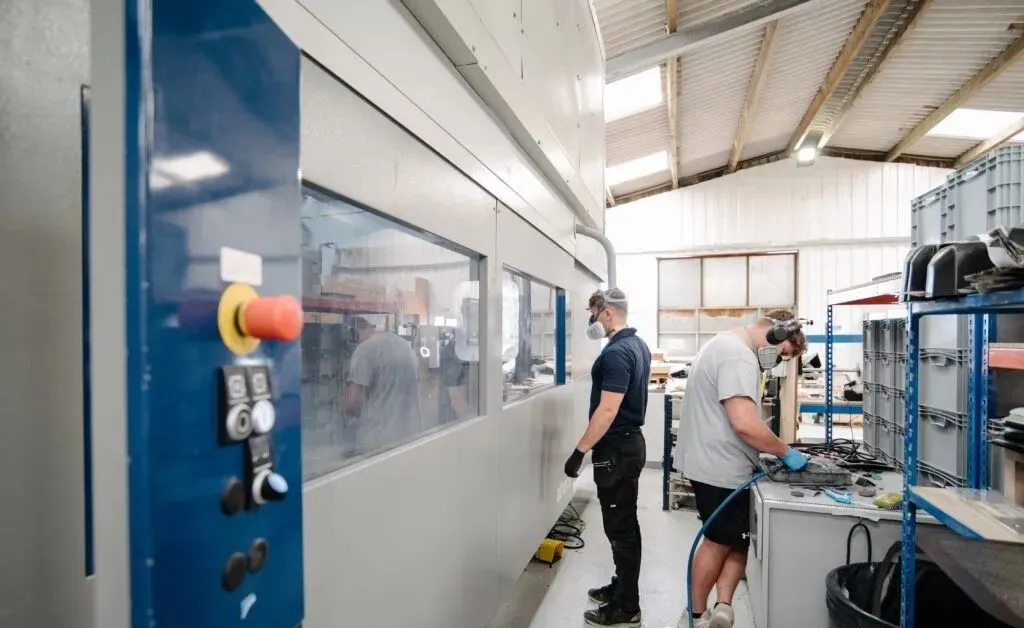
The composite manufacturing process varies according to the expected yield of the material and the final composite. The three main composite manufacturing processes are open molding, closed molding and perfusion molding. Then, there are multiple processing methods within each method. The decision of which composite manufacturing method to use is made based on the material, design and application of the final composite.
With the growing demand for such durable, robust and lightweight products, many industries are turning to composite materials. But one question that is often asked is “How are composites made?” Below, we explain in more detail the various methods that should enable you to make a more informed decision when choosing your preferred composite.
What is Composite manufacturing?
In short, composite fabrication is the process required to produce the final composite material. There are many technologies available, and the composite fabrication method chosen will always be driven by the final desired output, taking into account the required materials and design.
How are composites made?
Due to advances in composite manufacturing and process design, there are many ways to manufacture composite materials. From hand lamination to filament winding, pultrusion and weaving to 3D printing, the route to getting the final composite material fit for purpose is often customized. This ensures that the finished product matches the specifications of a particular project.
However, the fact that two very different techniques can produce seemingly identical results only adds to this already complex process. Below we pick out some of the most commonly used composite manufacturing processes, each very different and suitable for a range of sizes and types of finished parts.

Closed mold composite material manufacturing process
The closed-form composite manufacturing process involves manufacturing parts or products in closed or sealed molds that provide a controlled environment for curing or solidifying the composite. The process has the advantages of precise material control, higher fiber volume fraction, improved mechanical properties, reduced emissions, and suitable for the production of complex parts.
Closed mold composite material manufacturing method:
- Prepreg molding
This process is widely used and is gradually replacing traditional metal materials, especially in the aerospace industry. Prepreg is a composite manufacturing process that requires impregnation of reinforcing fibers such as carbon fiber, glass fiber, or aramidon fiber. During the composite manufacturing process, the prepreg is carefully placed in a mold or tool, and then precise heat and pressure are applied to cure the resin, resulting in the formation of the desired composite structure and the production of a composite with superior strength and properties.
The resin pre-impregnation process of the fibers is carefully carried out in a controlled environment, ensuring full impregnation at the specified resin ratio and distribution. This meticulous approach ensures optimum quality and reliability.
- Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
This particular composite is manufactured by mixing a reactive resin and then injecting it into a mold under pressure. Similar to injection molding, but using a pump or pressure tank to force the resin in at a fairly high pressure. Such injection pressures are usually around 10-20 bar (150-300psi), but in some high production methods they can be as high as 100bar (1,500 psi), which is quite a pressure!
This high pressure is then maintained until the resin cures in a mold, which is usually bolted or clamped together in a large hydraulic press with a flat plate. These ensure that the mold remains aligned during curing. Ideal for complex parts, RTM is a composite manufacturing process that is widely used in a wide range of industries such as the automotive industry.
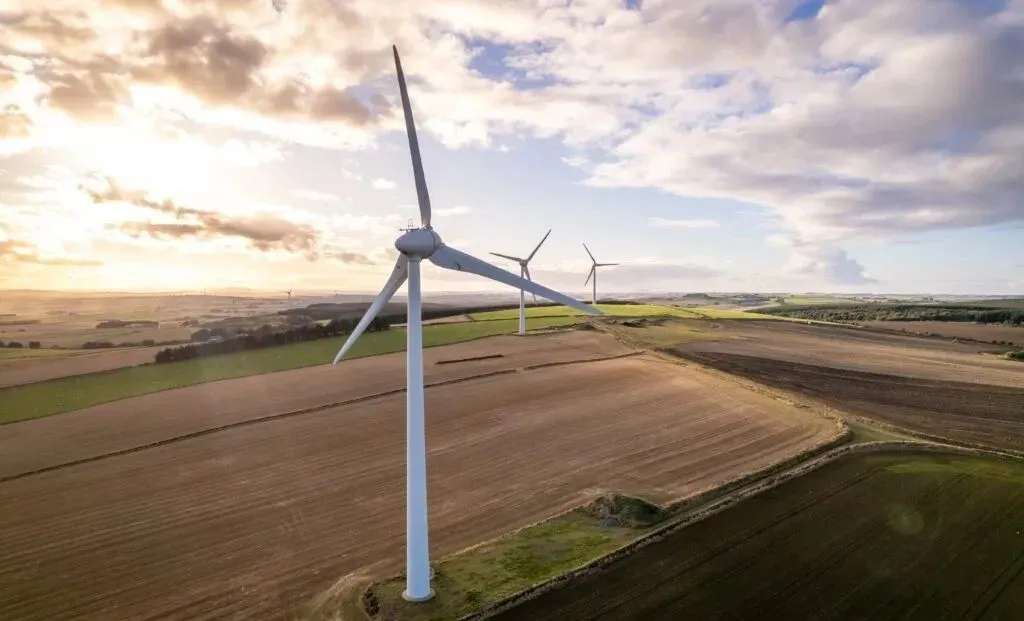
- Vacuum perfusion Vacuum perfusion
Ideal for hull hulls or wind turbine blades for the manufacture of low-viscosity resins, which are then impregnated with fibre preforms. A bunch of dry fiber-reinforced material is put into the mold, followed by a vacuum bag with a piping system on top. A vacuum is then extracted to allow the difference in pressure between the inside and outside of the bag to push the resin into the dry laminate.
This vacuum process forces the resin across the surface of the billet, penetrating into the thickness, thereby minimizing the distance the resin must travel across the billet.

- Compression molding
Compression molding is ideal for fairly small products that require a fully formed geometry and can be done using thermosetting or thermoplastic resins as well as a variety of different fiber types and lengths.
The process itself is to place the charges of the fiber and resin into a preheated mold, which is closed and kept under pressure until the resin cures. Class A surface finish can be achieved, and this composite manufacturing method is particularly suitable for the automotive industry. - Injection molding
Injection molding is arguably the most widely used net molding manufacturing process in composite materials. Bulk molding plastics are heated before being injected into heated molds and held under pressure until the resin cures.
Injection molding is mainly used for fairly small parts and can be mass-produced at low cost for high-precision parts that require specific geometry. Such products are already widely used in baby care products, medical devices, electronic devices and aviation. With advances in composite manufacturing and design processes, more and more materials are being used for injection molding to meet the growing demand for a variety of plastic products. - Autoclave forming
This is a closed-form composite fabrication tool that uses pressurized steam to perform a range of processes. By creating a high-pressure environment inside the autoclave, accurate results with the desired fiber content can be produced. The process itself involves curing the raw material in a double-sided mold or, in some cases, in a deoxidized vacuum bag.
Both processes are capable of producing large amounts of material, which makes this a process well suited for large facilities. Autoclave molding ensures a consistent hardening of the polymer, which makes it ideal for manufacturing composite materials. After the mold surface is coated with a release gel, the fiber textiles are placed into the mold, these are prepregs and therefore have been impregnated with resin.
Once the mold is filled, air is pumped out of the cavity and the entire assembly is placed in a vacuum bag. After all air has been removed from the bag, the container is placed in an autoclave to begin the curing process. The temperature and pressure increase slowly while curing, which hardens the material while removing pores. From here, the product is transferred to the oven, where its durability will be further enhanced.
Due to its good uniformity, the autoclave composite manufacturing process is often used to produce high strength ratio parts. For example, it will be used in aircraft components as well as in the military, Marine industry, spacecraft and missiles.
7.Braiding is a manufacturing method for narrow textile composites.
Woven fabrics are used in many end products, including clothing, shoes, ropes, and cables. This is an ideal method for developing seamless cylindrical fabric reinforcement materials to develop composite structures, and as a rapid manufacturing process that reduces waste, it is the perfect composite manufacturing process for many projects.
Extremely strong braided composites are known for their superior toughness and durability, especially when compared to fiber wound composites. They are used in a variety of applications from aerospace to prosthetics, and a range of woven fabrics with multiple configurations can be manufactured using carbon fiber, glass, aramid and mixed fiber systems.