Aramid paper honeycomb core material, which adopts the hexagonal structure of bionic natural honeycomb, is highly praised for its excellent specific strength, specific stiffness and structural stability. In addition, the material has excellent sound insulation, heat insulation, and flame retardant properties, with very low smoke and toxicity during combustion. These properties have given it a place in high-end applications in aerospace and high-speed transportation vehicles.
Despite the high cost of aramid paper honeycomb core, it is often selected as a key lightweight material for high-end equipment such as aircraft, missiles and satellites, especially in the manufacturing of structural components requiring broadband wave transmission performance and large rigidity and secondary stress.
Lightweight benefits
Aramid paper, as a key airframe structural material, plays a crucial role in major low-altitude and economical aircraft such as EVTors, especially as a carbon fiber honeycomb sandwich layer, which has been widely adopted by the world’s leading eVTOL manufacturers, such as Joby, Archer, Ehang and Fengfei.
In the field of UAV, Nomex honeycomb material (aramid paper) is also widely used, it is used in the body shell, wing skin and leading edge. For example, the French-built Orkor multi-purpose UAV Jackal 2 prototype uses a glass fiber/carbon fiber/arylon fiber composite design.
The landing gear and pipe structure parts of UAV displayed by Tai He New Material at Shanghai Composite Exhibition are made of aramid composite materials. These parts are prepared by the tube rolling process of aramid prepreg, which is mainly used for low-altitude aircraft and has the characteristics of lightweight and high toughness.
Performance of protection
The application of aramid fiber in the protective components and bulletproof armor of Uavs significantly improves the survivability of Uavs in harsh environments and protects key components from damage.
In addition to reinforcing materials such as carbon fiber, glass fiber and aramid fiber, sandwich structural materials such as honeycomb, adhesive film, foam and foam are widely used in the manufacturing process of low-altitude aircraft, such as UAV.
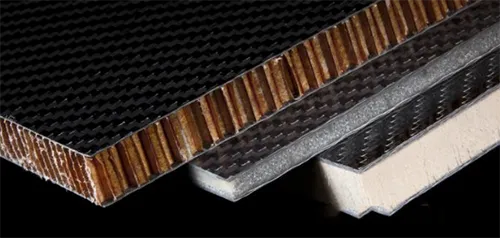
In the choice of sandwich materials, the commonly used honeycomb sandwich (such as paper honeycomb, Nomex honeycomb, etc.), wood sandwich (such as birch, tongwood, pine, linden wood, etc.) and foam sandwich (such as polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene foam).
Foam sandwich structure has been widely used in UAV body structure because of its waterproof and floating characteristics and technological advantages of being able to fill the internal structure cavity of wing and tail as a whole.
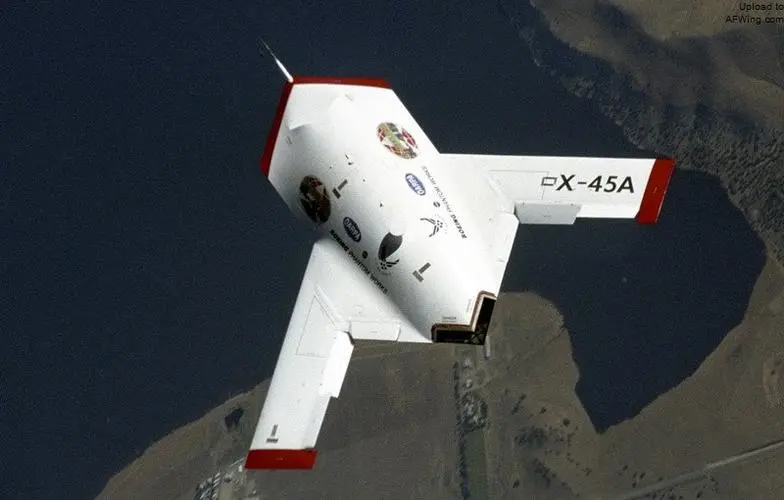
Taking the X-45A unmanned fighter aircraft developed by Boeing of the United States as an example, its fuselage uses low-temperature curing prepreg, while the wing uses foam resin sandwich (FMC) technology, which significantly reduces the manufacturing cost and cuts it by half compared with traditional methods.

In the design of low-speed UAV, honeycomb sandwich structure is usually used for components with low strength requirements, regular shape, large curved surface and easy to lay, such as front wing stabilizer, vertical tail stabilizer and wing stabilizer. For parts with complex shapes and small curved surfaces, such as elevator surface, rudder surface, aileron rudder surface, etc., the foam sandwich structure is preferred. For mezzanine structures that require higher strength, wooden mezzanine may be selected.
For those parts that require both high light and high stiffness, such as fuselage skin, T beam, L beam, etc., laminate construction is usually used. The manufacturing of these parts requires preforming and selecting appropriate reinforcement fibers, matrix materials, fiber content and laminates according to the required in-plane stiffness, bending strength, torsional stiffness and strength requirements, as well as designing different laying angles, layers and lay-up sequences, and curing through different heating temperatures and pressure.



I?¦m now not sure the place you are getting your info, however great topic. I needs to spend a while learning much more or figuring out more. Thank you for excellent info I was on the lookout for this info for my mission.